For 365 days a year, 24 hours a day, the Sentinels of the European Copernicus Earth Observation programme scan the surface of our planet.
The satellites that make up this constellation orbit at an altitude of more than 400 kilometres, searching for fires and help to grasp the extent of flooding, damage due to earthquakes, or they provide public institutions with help in emergencies, as happened in the case of the lockdown brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Since 2012, e-GEOS, a company set up by Telespazio (80%) and the Italian Space Agency (20%), has worked with the European Commission, the European Space Agency, and the European Environmental Agency (EEA) to acquire and support processing of satellite data from the Sentinel 1 and Sentinel 2 missions.
In particular, e-GEOS acquires images from the two missions via the Matera Space Centre, in Italy, one of the ESA's three Core Ground Segment stations – along with Mas Palomas, on Gran Canaria, and the Svalbard station in Norway.
Both the Sentinel 1 and Sentinel 2 missions are made up of two satellites, but they differ in terms of the eyes with which the four satellites look at the planet: synthetic aperture radar (SAR) for Sentinel 1, and an optical sensor for Sentinel 2 satellites.
e-GEOS's image acquisition activity began in April 2014, following the launch of the first Sentinel 1, and increased gradually over the years that followed, with the completion of both constellations. With the launch of Sentinel 2B, in March 2017, Matera began to work at full capacity and to acquire about 530 images per month from the four satellites.
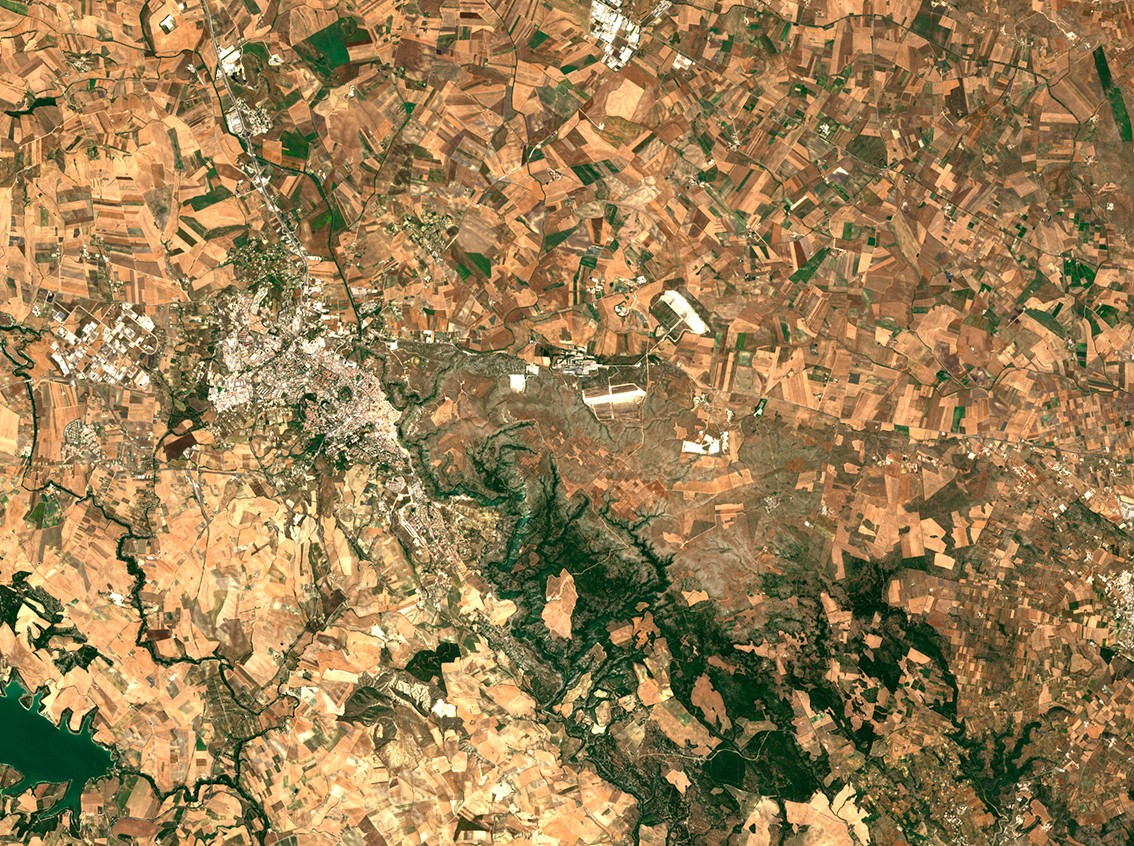

An optical image of Matera, Italy, captured by Sentinel 2
From Space, for the citizens
Thanks to the data provided by Copernicus, European Institutions have created services to make the best use of the space infrastructure's characteristics, to the advantage of all citizens.
For example, thanks to the Emergency Management Service (EMS), for which e-GEOS guides a European consortium that also involved its subsidiary GAF and Telespazio Iberica, images can be acquired and satellite maps can be provided, that are of fundamental importance for managing rescue operations. To date, e-GEOS has received more than 450 activations supporting international civil defence bodies, following emergencies and natural disasters.
But the sentinels also play an important role in defending the seas, both in the quest to combat pollution, as well as illegal fishing. In fact, e-GEOS uses Sentinel 1A and 1B, to scan the surface of our seas, looking for suspicious vessels or oil spills as part of the service provided by the European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA) and the Italian Environment Ministry.
In this case too, the images are acquired in Matera and, after being analysed and produced, they are distributed within 30 minutes of the satellite passing over the area involved, using a Near Real Time approach.
But that's not all, because besides its contribution to related services, e-GEOS has also played a part in important milestones in the entire Copernicus programme: in Matera, for example, the first data was obtained from the Sentinel-1A, Sentinel2A and Sentinel-1B satellites during the IOV (In-Orbit Validation) phase, of checking functioning of the systems on board the satellites.
Collaboration that is renewed
The collaboration between e-GEOS and the European Institutions responsible for Copernicus began in 2012 after an international tender process, and was recently renewed through to December 2021.
In fact, in April 2020, e-GEOS was awarded the contract put out to tender by the ESA for continuing data acquisition activities, from June 2020 through to the end of 2021.
More specifically, e-GEOS will provide services related to the activities of the Sentinel 1 mission, while those related to the Sentinel 2 mission continue, at this time, in terms of an extension of the previous contract.
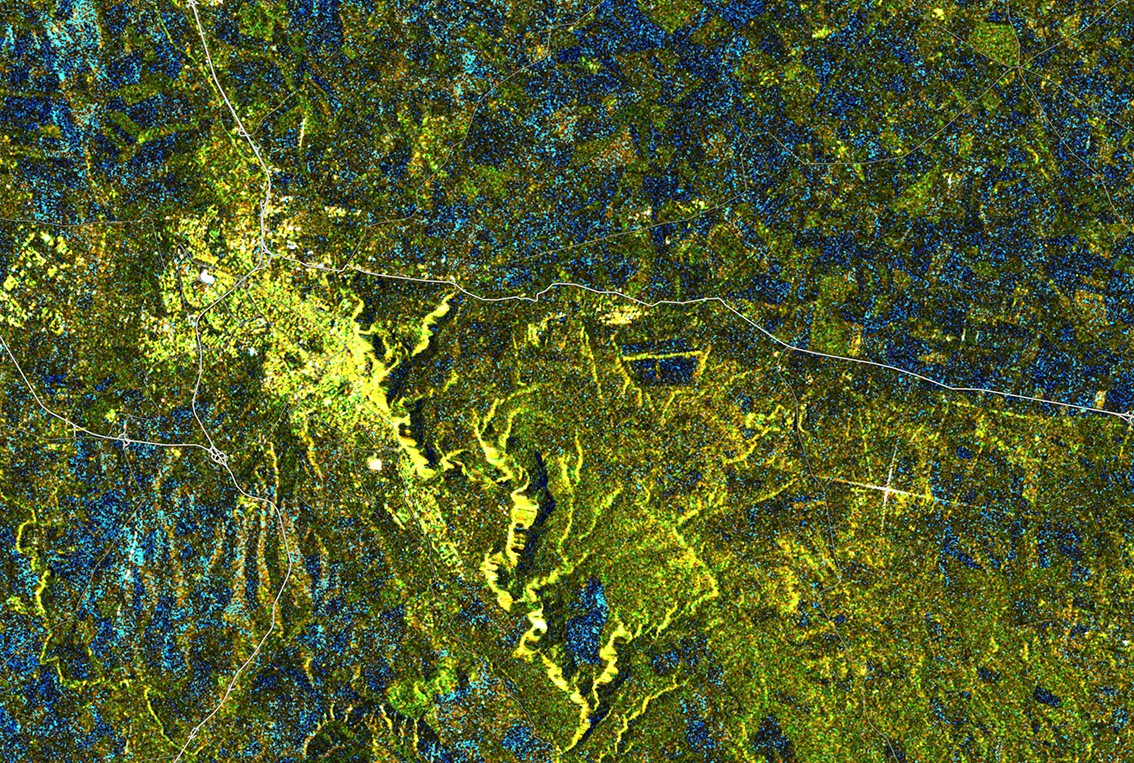
A SAR image of Matera, Italy, captured by Sentinel 1
A Group programme
Telespazio's involvement in the Copernicus programme does not stop with e-GEOS's role, but involves all the Group's skills.
In particular, Telespazio takes part in the Copernicus programme by providing setting up, maintenance, and evolution of the Payload Data Ground Segment (PDGS) for the Sentinel 1 and Sentinel 3 missions (via its subsidiary Telespazio Deutschland), of the Mission Control System for Sentinel 1, Sentinel 2, Sentinel 3 and Sentinel 5P, and the infrastructure for accessing the Earth Observation products from the Copernicus missions (Copernicus Space Component Data Access/Coordinated Data Access System - CSCDA/CDS).
In the operations sector, Telespazio personnel support the ESA's European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) during the pre- and post-launch phases of the Sentinel satellites, and is responsible for the CSCDA/CDS operations.
In addition, through to the end of 2021, Telespazio is responsible for managing ground segment operations for the Sentinel 3 mission.